|
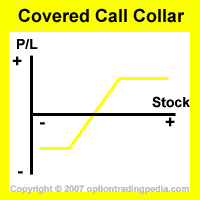
Learn How To Read This Chart
Covered Call Collar - Introduction
A covered call collar is an improvement made on top of a covered call. A complete understanding of Covered Call is needed in order
to understand what a covered call collar is.
A Covered Call suffers unlimited losses when the underlying asset drop in price drastically. In order to hedge against such a move, a Covered Call
Collar buys a put option
on top of the covered call position such that if the underlying asset should drop in price, the put option will gain in price
proportionally, thereby hedging against the loss. Therefore, a Covered Call Collar, or simply known as a Collar, is a Covered Call with limited maximum loss.
In options trading, the more hedged and multi-directional a position is, the lower the maximum profit potential becomes. This is the same
trade off in a Covered Call Collar. A part of the profits obtained from the sale of the
call options in the covered call needs to be
committed to the purchase of
put options in order to
hedge downside risk,
transforming the Covered Call into a Covered Call Collar position.
In fact, veteran options traders would immediately notice that the Covered Call Collar is actually a
Conversion closing out a
Synthetic Short Put position.
When significant price discrepancies between the call and put options exist, the Covered Call Collar position actually
becomes a
Conversion Arbitrage
position, sealing in risk-free profits.
When To Use Covered Call Collar?
One should use a covered call collar when one wishes to profit when the underlying asset is up or stagnant and to protect against a drop
in price of the underlying asset .
How To Use Covered Call Collar?
Establishing a covered call collar is extremely simple. All you have to do is to write (sell to open) 1 contract of nearest out of the money call option
for every 100 shares you own and then buy to open 1 Out of the Money (OTM) Put option for every 100 shares you own.
|
Example : Assuming you own 700 shares of QQQQ at $44. Sell To Open 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call. Buy to Open 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan42Put.
|
Profit Potential of Covered Call Collar:
The Covered Call Collar's maximum profit occurs when the stock closes exactly at the strike price of the short call options at expiration of the short call options. Its maximum
profit will be lower than a Covered Call because part of that profit has been spent towards purchasing a downside protection in the form of the OTM
put option.
|
From the above example : Assuming your 700 QQQQ close at $45 upon expiration of the 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call. You will make the $1 gain in QQQQ plus the
value of the 7 Jan45Call that you wrote, less the total price paid towards the purchase of the put options as it expires out of the money.
|
Such an ideal situation is, of course, rare. In most cases, the short call options will either be in the money or out of the money at expiration.
When your stock is stagnant or slightly higher upon expiration of the short call options, you will profit on the whole value of the call options that you wrote, with whatever profit from the stock if it is up slightly.
|
From the above example : Assuming your 700 QQQQ close at $44.50 upon expiration of the 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call. You will make the $0.50 gain in QQQQ plus the
value of the 7 Jan45Call that you wrote, less the total price paid towards the purchase of the put options as it expires out of the money.
|
When your stock has gained in price beyond the strike price of the short call options upon expiration, your stocks will be called off (assigned) and you will profit from the value of the call options that you wrote and the
value of the stock up till the strike price of the short call options. That is to say, you will not benefit from any rise in your stock beyond the strike price of the short call options due to the short call options going in the money.
|
From the above example : Assuming your 700 QQQQ close at $46 upon expiration of the 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call. You will gain the value of the
7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call that your wrote, less the total price paid towards the purchase of the put options as it expires out of the money.
Your 700 shares of QQQQ will be called off (bought by the person whom you sold the call option to)
at $45 (the strike price of the QQQQ Jan45Calls that you sold.) You will therefore make $1 from your stock, not $2.
|
From the below profit calculations of the covered call collar, you will learn that you will make more profits if your stocks are assigned rather than when your stocks are not assigned. This is of course
a disadvantage if you would like to keep the stock for the long term.
Trading Level Required For Covered Call Collar
A Level 1 options trading account that allows the execution of Covered Call and Protective Put is needed as the Covered Call Collar is a combination of both strategies. Read more about Options Account Trading Levels.
Profit Calculation of Covered Call Collar:
1. If stocks are not assigned (called off) at expiration:
Profit = (value gained in stock + initial price of short call options - purchase price of OTM put options) / initial value of underlying stock
Assuming you bought 700 QQQQ close at $44, sold 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call for $1.00 and bought 7 contracts of Jan42Put for $0.35.
Assuming at expiration, QQQQ closes at $44.50.
Profit = ($0.50 + $1.00 - $0.35) / $44 = 2.61%
|
2. If stocks are assigned (called off) at expiration:
Profit = ((strike price of short call options - initial value of underlying stock) - purchase price of OTM put options + initial price of short call options) / initial value of underlying stock
Assuming you bought 700 QQQQ close at $44, sold 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call for $1.00 and bought 7 contracts of Jan42Put for $0.35.
Assuming at expiration, QQQQ closes at $46.00.
Profit = (($45 - $44) - $0.35 + $1.00) / $44 = 3.75%
|
3. If stocks have dropped in value at expiration but long put options remain out of the money:
Profit = (initial price of short call options - (initial stock price - stock price at expiration)) - purchase price of OTM put options) / initial value of underlying stock
Assuming you bought 700 QQQQ close at $44, sold 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call for $1.00 and bought 7 contracts of Jan42Put for $0.35.
Assuming at expiration, QQQQ closes at $43.50.
Profit = ($1.00 - ($44 - $43.50)) - $0.35) / $44 = 0.34%
|
4. If stocks have dropped in value at expiration and long put options are in the money:
Maximum Loss = (((initial price of underlying asset - strike price of OTM put option) + Purchase price of OTM put option) - initial price of short call options) / initial value of underlying stock
Assuming you bought 700 QQQQ close at $44, sold 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call for $1.00 and bought 7 contracts of Jan42Put for $0.35.
Assuming at expiration, QQQQ closes below $42.00.
Maximum Loss = (($44 - $42) + $0.35) - $1.00) / $44 = 3.06%
|
Risk / Reward of Covered Call Collar:
Upside Maximum Profit: Limited
Maximum Loss: Limited
Break Even Point of Covered Call Collar:
There are 2 ways to look at breakeven point for a covered call collar.
1. As the Covered Call Collar profits mainly from the decay of the short out of the money call options, the main way to look at breakeven is
the number of days it takes for the decay of the short call options covers its bid/ask spread and the purchase price of the out of the money put options.
Stagnant Breakeven point = (Bid ask spread of short call option + Purchase price of OTM put option) / theta
Assuming the ask price of the short call option is $1.00 and bid price is $1.05 with a theta of -0.012.
Stagnant Breakeven Point = ($0.05 + $0.35 / 0.012) = approximately 33 days.
|
2. The lower breakeven point to find out how much the underlying stock can fall before you start making real losses to your account value.
Lower Breakeven point = (Initial Value of Short Call Options - Purchase price of long OTM put option) - Initial Value of underlying stock
Assuming you bought 700 QQQQ close at $44 and sold 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan45Call for $1.00 and bought 7 contracts of Jan42Put for $0.35.
Lower Breakeven Point = (($1.00 - $0.35) - $44) = $43.35
|
Advantages Of Covered Call Collar:
Able to profit even if your stock stays stagnant.
Able to offset losses if your stock drops in value.
Loss is limited even if underlying asset drops in price drastically.
Disadvantages Of Covered Call Collar:
You must continue to hold your stocks if you want to keep the short call options.
You can lose your stocks if it rises beyond the strike price of the short call options through assignment at expiration.
A narrower lower breakeven than a Covered Call.
Lower potential profit than a Covered Call.
Alternate Actions for Covered Call Collars Before Expiration :
1. If you wish to keep your stocks when it has gained in price beyond the strike price of the short call options, you could buy back
the short call options before it expires and allow the stock to continue its profit run.
2. In addition to keeping your stocks using the action above, you could also use the excess money after the buy back to buy put options
at the money in order to protect the current profits of the stock. This is known as a Protective Put.


|
High Yield Covered Call: Finding the Perfect Stocks For Covered Calls
Wondering how to look for the perfect stock for writing Covered Calls on? Wondering how many ways there are to write Covered Calls?
Want to learn about the 2 ways to measure Covered Calls returns and also how to automatically look for high yield Covered Call opportunities?
This $29.90 eBook teaches you all these and more! ONLY $29.90 and you could be making hundreds this very month from this knowledge!
See More Ebooks!
Average Reader Rating : 4.5 / 5
www.Optiontradingpedia.com is a Masters 'O' Equity company and uses Masters 'O' Equity payment gateway
|
|
|