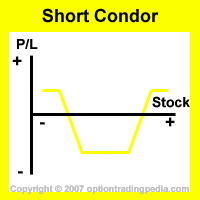
How Does Short Condor Spread Work in Options Trading?
Short Condor Spread - Introduction
The Short Condor Spread is an advanced credit spread
volatile option trading strategy where you get to keep the net credit if the underlying stock rallies or ditches.
As the name suggests, a Short Condor Spread is where you become the "Banker" in a Condor Spread transaction by selling a condor spread
to someone who is speculating on the same underlying stock being stagnant.
You need to understand how a Condor Spread
works before you can understand the dynamics behind the Short Condor Spread.
It is a cousin of the short butterfly spread
but involves 4 strike prices instead of 3 strike prices.
|
|
Because the Short Condor Spread involves 4 strike prices instead of just 3 as in the Short Butterfly Spread, the Short Condor Spread's breakeven points are further but with a slightly higher maximum profit potential. In fact, the Short Condor Spread has the highest profit potential amongst the family of complex volatile option strategies.
Comparing The Short Condor Spread...
The Short Condor Spread belongs to the family of complex volatile option strategies, similar to the Short Butterfly Spread, Reverse Iron Butterfly Spread and Reverse Iron Condor Spread. Each of them has their own strengths and weaknesses but they all have one thing in common, and that is, they all have narrower breakeven points than the basic Straddle / Strangle and a lower maximum loss than a Straddle even though their maximum profit potential is limited. Here is a table explaining the differences:
| Short Condor Spread | Reverse Iron Condor Spread | Short Butterfly Spread | Reverse Iron Butterfly Spread | |
| Debit/Credit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit |
| Max Profit | Highest | Higher | High | Low |
| Max Loss | Low | High | Higher | Highest |
| Cost of Position | NIL | High | NIL | Low |
| Breakeven Range | Wide | Widest | Narrow | Wider |
As you can see from the table above, all of the above complex volatile option strategies comes with their own strengths and weaknesses. Option trading strategies are all about trade-offs. There are no single option trading strategy that has the best of all worlds.
When To Use Short Condor Spread?
One should use a Short Condor Spread when one expects the price of the underlying asset to make a quick break to either upside or downside. One can use this strategy ahead of earnings releases or important releases.
How To Use Short Condor Spread?
There are two ways to establish a Short Condor Spread. One way is to use only call options. We call this a "Call Short Condor Spread". The other way is to
use only put options. We call that a "Put Short Condor Spread". Either way performs the same as long as the underlying asset breaks above or below the
upper or lower breakeven points upon option expiration.
(a)Sell One Far ITM + (b)Buy ITM + (c)Buy One OTM + (d)Sell One Far OTM
Establishing Call Short Condor Spread
Veteran or experienced option traders would identify at this point that the Short Condor Spread actually consists of a Bull
Call Spread and a Bear Call Spread. This is similar to a Short Butterfly Spread
except for the fact that the middle strike price has been splitted up into 2 different strike prices in order to set up a wider breakeven points and a higher profit.
The choice of which strike prices to sell the short legs (trades a and d above) at depends on how far the underlying stock is expected to break. The further
away from the money the 2 short legs are, the higher the risk (as the underlying stock needs to move further in order to exit the breakeven range), and the
higher the potential profits (as the further in the money options will yield a lot more credit).
A Short Condor Spread is therefore an extremely advanced volatile option strategy where an option trader gets to control both the breakeven points as well as the maximum loss range and amount with careful calculation.
|
Short Condor Spread Example
Assuming QQQQ trading at $43.57. Buy To Open 1 contract of Jan $43 Call at $1.63 Buy To Open 1 contract of Jan $44 Call at $1.03 Sell To Open 1 contract of Jan $45 Call at $0.60 Net Credit = ($2.38 - $1.63 - $1.03 + $0.60) x 100 = $32.00 per position |
In the above Call Short Condor Spread example, we are expecting the QQQQ to exceed a price range of between $42 to $45 upon expiratio, with maximum loss occuring when QQQQ is within $43 to $44.
Establishing Put Short Condor Spread
Establishing a Put Short Condor Spread is exactly the same as establishing a Call Short Condor Spread except that put options are used instead. The resultant net credit and breakeven range of a Put Short Condor Spread are theoretically the same as you would use call options in a Call Short Condor Spread, however, in practise, Call options and Put options do not cost the same to put on. In stocks that are likely to be more bullish, its call options will be more expensive than its put options and vice versa. Therefore, a trader needs to calculate whether a Call Short Condor Spread or a Put Short Condor Spread yields a higher credit with the same strike prices.
|
Put Short Condor Spread Example
Assuming QQQQ trading at $43.57 Sell To Open 1 contract of Jan $43 Put at $0.85 Sell To Open 1 contract of Jan $44 Put at $1.24 Buy To Open 1 contract of Jan $45 Put at $1.84 Net Credit = ($0.59 - $0.85 - $1.24 + $1.84) x 100 = $34.00 per position |
We see that the Put Short Condor Spread is more profitable to establish than the Call Short Condor Spread today, so the Put Short Condor Spread should be used instead. (However, we will continue to use the Call Short Condor Spread as a standard example for the rest of this article.)
Trading Level Required For Short Condor Spread
A Level 4 options trading account that allows the execution of credit spreads is needed for the Short Condor Spread. Read more about Options Account Trading Levels.
Profit Potential of Short Condor Spread :
Short Condor spreads achieve their maximum profit potential, which is the net credit received from putting on the positions, at expiration if the price of the underlying asset exceeds either the upper breakeven point or lower breakeven point. The profitability of a short condor spread can also be enhanced or better guaranteed by legging into the position properly.
Profit Calculation of Short Condor Spread:
Maximum Profit = Net Credit
Maximum Loss = Difference between consecutive strikes - credit
|
From the above Call Short Condor Spread example :
Maximum Profit = $32.00 Maximum Loss = $1 - $0.32 = $0.68 x 100 = $68.00 per position |
Risk / Reward of Short Condor Spread:
Upside Maximum Profit: Limited
Maximum Loss: Limited
Break Even Points of Short Condor Spread:
A Short Condor Spread is profitable if the underlying asset expires outside of the price range bounded by the upper and lower breakeven points.
1. Lower Breakeven Point : Credit + Lower Strike Price
|
Credit = $0.32 , Lower Strike Price = $42.00
Lower Breakeven Point = $0.32 + $42.00 = $42.32. |
And
2. Upper Breakeven Point : Higher Strike Price - Credit
|
Credit = $0.32 , Upper Strike Price = $45.00
Higher Breakeven Point = $45.00 - $0.32 = $44.68. |
Advantages Of Short Condor Spread:
Disadvantages Of Short Condor Spread:
Alternate Actions for Short Condor Spreads Before Expiration :
1. When it is obvious that the underlying stock is going to go up, you could buy back the short In The Money (ITM) call options
to maximise profits, essentially transforming the position into a Bull Call Spread with an additional call option on it.
2. If the underlying asset has dropped in price and is expected to continue dropping, you could sell the long call options and
hold the short call options. This action is only possible if your broker allows you to sell naked options.

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
| Javascript Tree Menu |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by